- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
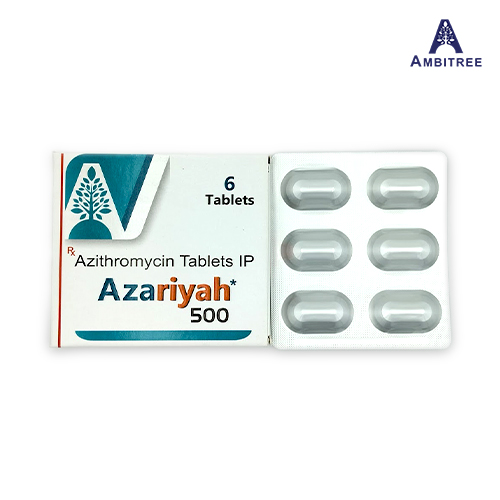
Azariyah-500
Azariyah 500 tablets contain Azithromycin, an antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Azithromycin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, effectively killing the bacteria causing the infection. It is commonly prescribed for respiratory tract infections, skin infections, ear infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Azariyah 500 provides effective treatment with a convenient dosage regimen, ensuring rapid recovery from bacterial infections when used as directed under medical supervision.
BENEFITS:
- Broad-spectrum Antibiotic: Effective against a variety of bacterial infections including respiratory infections, skin infections, ear infections, and sexually transmitted infections.
- Convenient Dosing: Typically requires a shorter course of treatment compared to other antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Can help reduce inflammation in certain infections.
HOW IT WORKS:
Azithromycin: Belongs to a class of drugs known as macrolide antibiotics. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which stops bacterial growth and eradicates the infection.
DIRECTIONS FOR USE:
- Take the tablet orally with or without food, usually once daily or as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your usual dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
SIDE EFFECTS:
- Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and headache.
- Serious: Severe allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness), difficulty breathing, irregular heartbeat, severe dizziness, and persistent diarrhea.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe side effects.
WARNINGS & PRECAUTIONS:
- Contraindications: Avoid use if allergic to azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, clarithromycin).
- Consultation: Inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions, especially liver disease, kidney disease, or heart problems. Provide a complete list of medications you are taking, including supplements.
- Interactions: May interact with other medications such as antacids, blood thinners, and certain antibiotics. Discuss potential interactions with your doctor.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep out of reach of children.
- Dosage Adherence: Ensure the full course of treatment is completed as prescribed, even if symptoms improve. Skipping doses or stopping early can lead to treatment failure and bacterial resistance.
Note: Always consult your doctor before taking any medication.
Vendor Information
- Address: